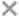
Other Names
- Australian Ghost Shrimp
- Ghost Nipper
- Marine Yabby
General Description
The large flattened claw of the male is almost as long as the animal itself and with a deep notch into the palm between the two fingers; the larger claw in females is simpler. Antennule peduncle much heavier and longer than antenna peduncle, article 3 about twice as long as article 2. Maxilliped 3 ischium-merus operculiform, merus projecting beyond articulation with carpus; propodus and dactylus digitiform. Male pleopod 2 absent. Body up to 6.5 cm long.
Biology
Ghost shrimps are used as bait by fisherman. A specially designed hand-held "yabby pump" is placed over the burrows in intertidal sandy mud and the inhabitants sucked out. Fishermen call these ghost shrimps Bass yabbies (after Bass Strait) or one-armed bandits (because of their one long cheliped). Recent studies on their behaviour show how useful these burrowing crustaceans are in keeping the sediment healthy and fisherman would be wise to select alternative bait and allow the ghost shrimps to continue their important work.
Habitat
Intertidal sand and mudflats, often estuarine.
Soft substrates
Distribution guide
Southern temperate oceans, including south-eastern Australia.
Species Group
Prawns, shrimps, lobsters › Ghost and mud shrimps
Depth
Water Column
Max Size
6.5 cm
Diet
Organic matter
Harmful
Not harmful but a nip from large claws could be painful
Commercial Species
No
Global Dispersal
Native to Australia
Species Code
MoV 1008
Conservation Status
- DSE Advisory List : Not listed
- EPBC Act 1999 : Not listed
- IUCN Red List : Not listed