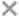
General Description
The species is notable for the small hook-like keel on the abdomen and a long hairy hand on the second walking leg of the male. Up to 15 mm long.
Biology
Gammarella berringar lives in sandy sediments in shallow bays and the continental shelf. The ways in which amphipods move depends on the arrangement of their legs. Most walk upright using most of the thoracic legs but this is very slow. Swimming using the three pairs of pleopods is much faster. The speciality of amphipods is the tail-flip, a rapid escape response where the abdomen flicks the animal away after the uropods are dug into the ground.
Habitat
Sandy sediments in shallow bays and the continental shelf, to depth of 27 m.
Soft substrates
Distribution guide
South-eastern Austria, including central and eastern Victoria.
Species Group
Depth
Water Column
Max Size
15 mm
Diet
Organic matter
Commercial Species
No
Global Dispersal
Native to Australia
Species Code
sp. MoV 365
Conservation Status
- DSE Advisory List : Not listed
- EPBC Act 1999 : Not listed
- IUCN Red List : Not listed