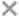
General Description
Body large robust, dorsal fin single, long-based; tail large almost square; lips thick, fleshy lips; teeth large, peg-like; scales large, heavy, and form scaly sheaths at the dorsal and anal fin bases. Adult males are greyish to blue, adult females are typically greyish-green to reddish in colour, and juveniles are greenish with scattered pale spots. To 1.8 m long, and a weight of up to 40kg.
Biology
These large inquisitive wrasses are benthic carnivores, feeding on small crabs and other crustaceans, echinoderms (sea urchins) and molluscs, including abalone. Like most wrasses, blue groper change sex from females to males during their life (protogynous hermaphrodites), and also change colour along the way.
Habitat
Exposed rocky reefs along the coast, to depths of 100 m, most in 0-40 m; juveniles shelter amongst seagrasses and macro-algae in bays and estuaries.
Reefs
Seagrass meadows
Distribution guide
Southern Australia, including western and central Victoria.
Species Group
Fishes › Wrasses, rock whitings and allies
Depth
Shallow (1-30 m)
Deep ( > 30 m)
Water Column
Max Size
1.8 m
Commercial Species
Yes
Global Dispersal
Native to Australia
Identify
Conservation Status
- DSE Advisory List : Not listed
- EPBC Act 1999 : Not listed
- IUCN Red List : Vulnerable